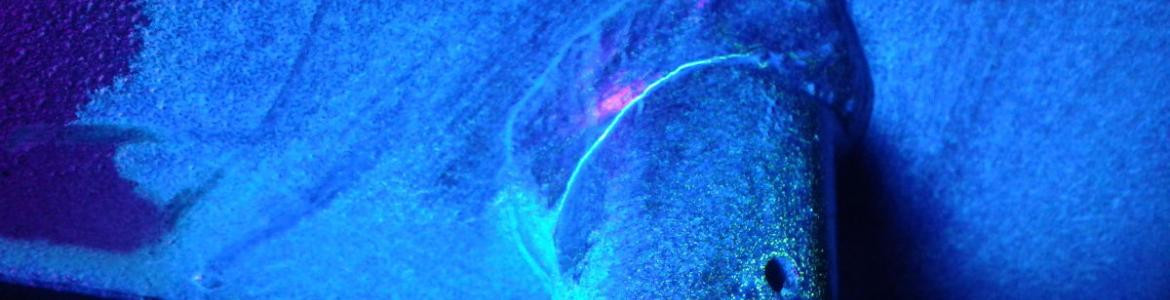
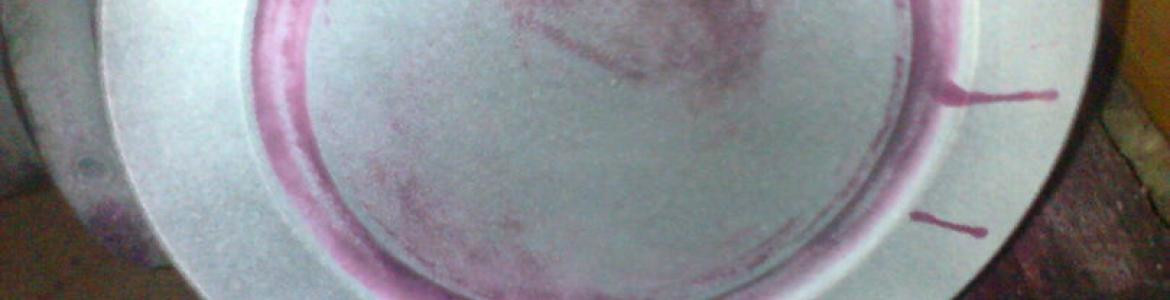
Magnetic Particles Testing
Magnetic particles Testing (MT) allows for quick and reliable detection of any surface defects in ferromagnetic materials, caused by cracks, heterogeneous structure, foreign insertations, material discontinuities.
This method is applied when detecting flaws at (the so-called "open flaws") or near ("closed flaws") the surface of the test piece. It may be used at elements with thin galvanic coatings.
Dye-penetrant testing method
Penetration method (PT) allows for fast and easy detection of discontinuities - surface flows on such metallic materials as: steel, cast steel, cast iron, light metals, non-ferrous metals etc.; as well as non-metallic eg.: ceramic.
Fluorescent penetration method - the inspections are done in ultraviolet light, the sources of which are appropriate devices: UV-lamps.
Ultrasonic Testing Metod
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) uses occurances attendant upon generation and diffusion of mechanical vibrations supersonic frequency, i.e. over 16000 Hz.
In the ultrasonic method the mechanical vibrations are generated and introduced into the inspected unit with an ultrasonic probe. The probe is applied to the inspected surface through a thin layer of liquid, gel or oil that would act as a couplant.
Visual Inspections
Visual inspections enable detection of the products` deficiencies such as shape defects, dimensional inconsistencies and inappropriate assembly, as well as inspection for surface discontinuities caused during the production process (cracks, porosity, rivets, lappings, undercuts, inclusions, incomplete fusions etc.). Other defects, such as system and component wear, corrosion, erosion, fatigue cracks, leaks etc. can also be detected visually. Fields of application of the visual inspection range from energetics to the operations of customs offices.